Chainlist MetaMask TechEduByte: Add Networks Safely (Desktop + Mobile)
MetaMask is a popular Web3 wallet, but it only works smoothly when the right network details are in place. Many searches for chainlist metamask techedubyte come from users who want to add a chain quickly, switch networks, and keep dApps working.
Chainlist can speed up setup by showing fields like Chain ID, RPC URL, and a block explorer link in one place. That convenience helps beginners, but it does not remove the need to verify information. MetaMask warns that it does not verify custom networks end-to-end, so the user remains responsible for checking the details.
Security pressure is also rising. Chainalysis reported record levels of crypto crime activity in 2025, and major thefts continued through 2025. For that reason, this guide focuses on clear steps, simple checks, a manual backup method, and troubleshooting that fixes problems in minutes.
What Is Chainlist and Why Does It Matter?
Chainlist is an online directory that helps users find network details needed to connect a wallet like MetaMask to different EVM-compatible blockchains. Instead of searching multiple sources, it typically shows the key fields MetaMask requires: Chain ID, RPC URL, currency symbol, and a block explorer link. These details tell MetaMask where to send requests (via JSON-RPC), how to identify the chain, and where to view transactions and blocks.
It matters because network setup errors are common. A wrong Chain ID, a broken RPC endpoint, or a misleading explorer link can cause failed transactions, missing balances, or unsafe connections. Chainlist reduces manual typing mistakes and speeds up switching between chains, especially for users who work across multiple networks. The smart approach is to treat Chainlist as a convenience tool and still verify the details before approving anything in MetaMask.
How does chainlist metamask techedubyte add a network in 60 seconds?
Users searching chainlist metamask techedubyte usually want a fast setup that avoids guesswork. The quickest safe method is a six-step flow plus a short verification checklist.
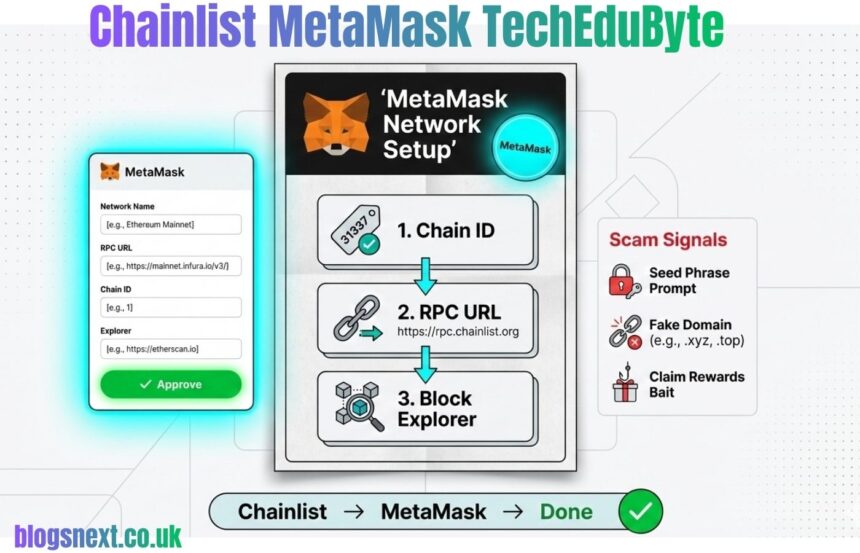
Quick Start (6 steps): (1) Open Chainlist in a trusted tab and bookmark it. (2) Connect MetaMask. (3) Search the network name and confirm mainnet vs testnet. (4) Click Add Chain. (5) In the MetaMask popup, review the fields. (6) Switch networks and run a small test action.
Verify before approving: confirm the Chain ID matches the intended chain, the RPC URL uses HTTPS and looks reputable, and the block explorer link opens the correct network. Reject any unrelated signature request. If any field looks unusual, stop and use the manual method instead. This habit prevents most setup errors and malicious RPC risks.
 How should users use Chainlist with MetaMask on desktop and mobile?
How should users use Chainlist with MetaMask on desktop and mobile?
A reliable chainlist metamask techedubyte workflow looks slightly different on desktop and mobile, mainly because connection prompts behave differently.
Desktop (extension): open Chainlist, click Connect Wallet, select MetaMask, search the network, then click Add Chain. When MetaMask opens the add-network modal, verify Chain ID, RPC URL, and block explorer. Approve and switch networks.
[Screenshot: Chainlist search] [Screenshot: MetaMask add-network modal]
Mobile (app): use MetaMask’s in-app browser instead of a random external browser tab. Visit Chainlist, connect the wallet, search the network, then tap Add Chain and review the same fields. If the button is missing or the app loops, close the app, reopen it, switch to Wi-Fi, and retry. This reduces broken prompts and failed connections significantly. Finish by testing a small action before moving funds.
How can users add a MetaMask custom network when Chainlist fails?
When Chainlist fails to connect, the safest backup is manual setup inside MetaMask. MetaMask’s help center shows both extension and mobile paths for adding a custom network and even adding extra RPC endpoints.
On the extension: open the network selector, choose Add network, and switch to custom networks. Enter Network name, RPC URL, Chain ID, currency symbol, and block explorer URL, then save. If one endpoint is unreliable, MetaMask also allows adding another RPC URL for the same network.
On mobile: open the network selector, tap Add Network, switch to Custom networks, and enter the same fields. Avoid copying RPC details from random posts; prefer official docs or reputable providers. After saving, switch networks and run a small test to confirm balances load correctly every time.
How can users stay safe and fix Chainlist MetaMask errors?
Security and reliability matter because wallet-draining scams and theft remain common. Chainalysis noted record crypto crime activity in 2025, and reports tracked multi-billion-dollar theft totals in 2025. That context makes careful network setup non-optional.
MetaMask recommends verifying custom network information, because the wallet does not fully verify that the network is honest. Use the three checks: Chain ID, RPC URL, and block explorer.
Troubleshooting quick fixes: if the RPC fails, switch to another endpoint or retry later; if Add to MetaMask is missing, disable ad blockers and unlock the wallet; if “Unknown network” appears, remove the entry and re-add with verified values. For performance, switching RPC can resolve slow balances and timeouts. Best practice: use a hardware wallet for serious funds and a separate test wallet for new networks.
What are the most common Chainlist MetaMask TechEduByte questions?
These FAQs address the most common questions people type after searching chainlist metamask techedubyte, such as safety, mobile support, and error fixes. Each answer starts with a direct response, then explains what to do next in plain language. The goal is to help readers complete the task, not just memorize terms.
For best results, readers should keep the same routine across networks: verify Chain ID, review the RPC URL, open the block explorer, and test with a small action before moving real funds. If something breaks, the fastest fix is usually switching the RPC endpoint or re-adding the network with verified details. When that fails, manual add in MetaMask can restore access, and saving the exact error text helps support forums diagnose the issue faster on desktop or mobile.
Is Chainlist with MetaMask safe to use?
Chainlist can be safe with MetaMask when the user treats it as a shortcut, not as a security guarantee. MetaMask states that it does not fully verify custom networks, even if basic validation passes, so users should verify the network information themselves.
The safest approach is the three-point check: confirm the Chain ID, review the RPC URL for a reputable HTTPS endpoint, and open the block explorer to confirm the chain is correct. If any field looks strange, the user should reject the request and add the network manually using official documentation.
Extra safety steps include bookmarking the official Chainlist domain, refusing any prompt that asks for a seed phrase, and testing with a small transaction before bridging or swapping. This method reduces exposure to phishing and malicious RPC endpoints.
How does someone add BSC to MetaMask using Chainlist?
To add BSC in the chainlist metamask techedubyte workflow, the user should search for “BNB Chain” on Chainlist and select the mainnet entry, not a testnet. After clicking Add Chain, MetaMask will display a network-add popup.
Before approving, the user should verify three items: the Chain ID matches BNB Chain mainnet, the RPC URL uses HTTPS and looks credible, and the block explorer link opens a BNB Chain explorer page. It also helps to confirm the currency symbol looks like BNB. If those details are correct, the user can approve the request and switch networks.
After switching, a quick test prevents surprises. The user should check that balances load, then send a small test transaction or open a known dApp to confirm the network works. If the RPC is slow, switching to another reputable endpoint usually fixes it.
 What is an RPC URL in MetaMask?
What is an RPC URL in MetaMask?
An RPC URL in MetaMask is the address of a server that answers wallet requests using JSON-RPC. MetaMask uses it to read balances, fetch block data, and broadcast transactions to the network. If the RPC is slow or unreliable, the wallet may show wrong balances, time out, or fail to send transactions.
A healthy RPC endpoint usually uses HTTPS, belongs to a reputable provider, and returns data for the expected chain. A suspicious RPC often uses odd domains, redirects, or returns a different chain than expected.
If a network feels “broken,” switching the RPC is a practical fix. On the MetaMask extension, users can add another RPC URL to the same network and set it as default. After switching, the user should reload the wallet and confirm the Chain ID and explorer still match the intended network.
What should someone do if the wrong network was added?
If the wrong network was added, the safest move is to remove it and re-add the correct one with verified details. Keeping a wrong network entry can cause dApps to connect to the wrong chain or show misleading prompts.
First, the user should open MetaMask settings, locate the network list, and remove the incorrect network. Next, the user should add the correct network either through MetaMask’s built-in list (if available), through Chainlist, or via manual entry. During re-addition, the user should confirm the Chain ID, review the RPC URL, and open the block explorer link.
After switching to the corrected network, the user should test with a small action. If balances still look wrong, the issue is often a token display problem. Adding the correct token contract for that network can restore visibility.
Why does MetaMask show “Unknown Network” after adding a chain?
“Unknown Network” usually means MetaMask cannot match what the RPC endpoint returns with the network details that were saved. In practice, this happens when the Chain ID is wrong, the RPC URL is misconfigured, or the endpoint is returning data for a different chain.
The fastest fix is to remove the network and re-add it using verified values. The user should confirm the Chain ID from an official source, then ensure the RPC endpoint belongs to a reputable domain and uses HTTPS. Opening the block explorer link helps confirm the network identity.
If the error appears only sometimes, the RPC may be unstable. Switching to a different endpoint often resolves it. After fixing the entry, the user should reload MetaMask, switch networks again, and test a small transaction. This confirms that dApps and explorers match the same chain.
Can custom networks be added if they are not listed on Chainlist?
Yes, MetaMask can add custom networks that are not listed on Chainlist, as long as the user has the correct network details. This is common for new rollups, private testnets, and niche EVM chains that are still early.
The user should open MetaMask and choose the custom network option, then enter a clear network name, a trustworthy RPC URL, the correct Chain ID, and a block explorer URL when available. MetaMask’s documentation also shows how to add more than one RPC endpoint, which helps when a single endpoint goes down.
Because unknown networks carry higher risk, verification matters even more. Users should only pull details from official project documentation or reputable infrastructure providers, not from random posts. After adding the network, testing with a small action confirms that balances load and transactions broadcast correctly.
Is Chainlist the best way to add networks to MetaMask?
Chainlist is often the fastest way to add a network, but it is not always the best way. The best method depends on what the user is trying to do and how much they trust the source.
If the network appears in MetaMask’s built-in list, using the native option is usually simpler and reduces connection friction. Chainlist is useful when the network is not listed, when the user needs to compare chain details quickly, or when adding several EVM networks in one session. Manual entry is best when Chainlist will not connect or when full control over the RPC URL is needed.
Regardless of the method, MetaMask advises users to verify custom network information and not assume safety. With rising scam activity reported in 2024–2025, verification is practical defense. A small test action should come before moving funds.
Why is the “Add to MetaMask” button missing on Chainlist?
This is commonly caused by an unlocked wallet requirement, ad blockers, or browser compatibility issues. Unlock MetaMask, disable ad blockers for the page, refresh, and try again. On mobile, use the MetaMask in-app browser instead of an external browser.
Conclusion: Chainlist MetaMask TechEduByte Next Steps
A solid chainlist metamask techedubyte workflow stays simple: use MetaMask’s built-in network add when available, use Chainlist to add networks faster when it helps, and fall back to manual entry when tools fail. The safest results come from a consistent verification habit. Before approving any add-network prompt, users should confirm the Chain ID, review the RPC URL for a reputable HTTPS endpoint, and open the block explorer link to confirm it matches the same chain.
After the network is added, a small test action should come before moving meaningful funds. If problems appear, switching to a healthier RPC endpoint or re-adding the network with verified values resolves most errors. Bookmarking trusted sources and keeping a separate test wallet for new networks reduces risk during everyday Web3 use.

 How should users use Chainlist with MetaMask on desktop and mobile?
How should users use Chainlist with MetaMask on desktop and mobile? What is an RPC URL in MetaMask?
What is an RPC URL in MetaMask?